
Turns the LED on digitalWrite(led2, HIGH) Defines the green LED as output pinMode(led2, OUTPUT) Defining the button pin as input pinMode(buttonPin, INPUT) Variable to check the state int buttonState Pin connected to push-button int buttonPin = A0
ARDUINO NANO PINOUT NUMBERS CODE
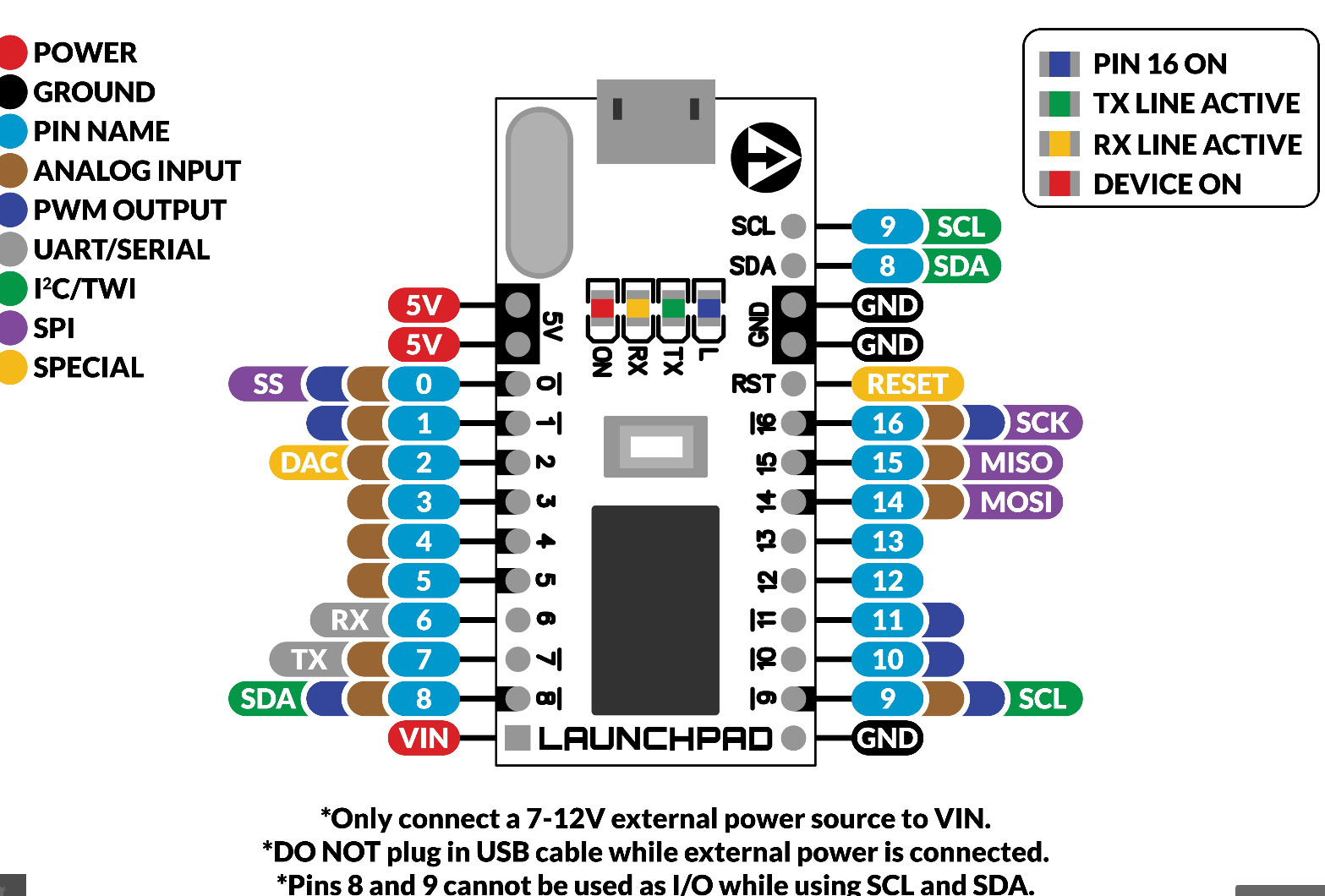
On the code below you can check out the comments to understand better how it works. After uploading the code, you can press the RIGHT button on the Interface Nanoshield to turn on one of the LEDs. If a button is pressed, do something and, if it is not, do another thing. If / else is really useful when you are dealing with digital outputs, which can only be in one of two states. Oops, the condition is false, do something else! if / else lets us take an action if the condition is true and another action if it is false. Let’s use the extension of the if-statement declaration, the else. Otherwise, you can store the value of digitalRead() inside a variable: You can use this return value as part of a conditional test inside an if-statement. The digitalRead() function will return one of the two values: high or low. So, instead of only writing the call to the function and jump to the next line, we really need to use this function along with other pieces of code. The digitalRead() function is different from the other ones, because it returns a value, which is the logic state of the pin. This way, it is not necessary to configure it again to use the function digitalRead(). On Arduino, by default, all the pins are already pre-configured as input. The digitalRead() works with all Arduino pins from D2 to D13 and from A0 to A5 (the only exceptions are the pins A6 and A7). There is only one parameter on digitalRead() - the number of the pin you want to read like, for example, digitalRead(A0) in order to read the logic state of the pin A0. It only tells us if the logic level is 1 or 0, which is sufficient when we work with digital systems. Notice that the digitalRead() function does not effectively measures the voltage at the pin. It is capable to tell wether the voltage at this pin is high (~ 5V) or low (~ 0V) or, in other words, if the pin is at logic state 1 or 0 (or HIGH/LOW). The digitalRead() function is used to read the logic state at a pin. Let’s introduce a new function, besides an addendum to if. They are connected to pin A0 on Arduino (further details on the next projects). The figure below shows the buttons on the Interface Nanoshield. The keys on a keyboard, for instance, are an input for your computer, because they send data to this system. Some of the common input components are buttons or switches. The inputs are signals or external values sent to a system.
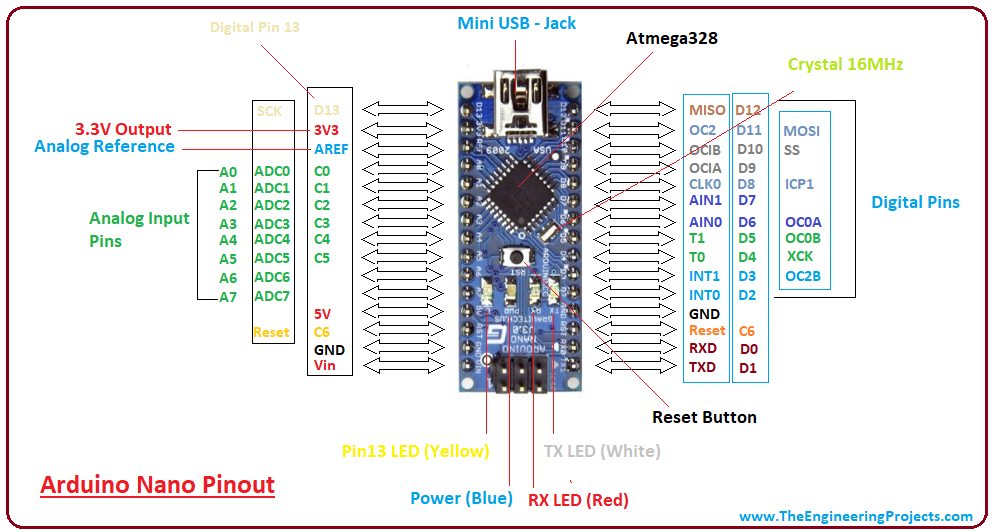
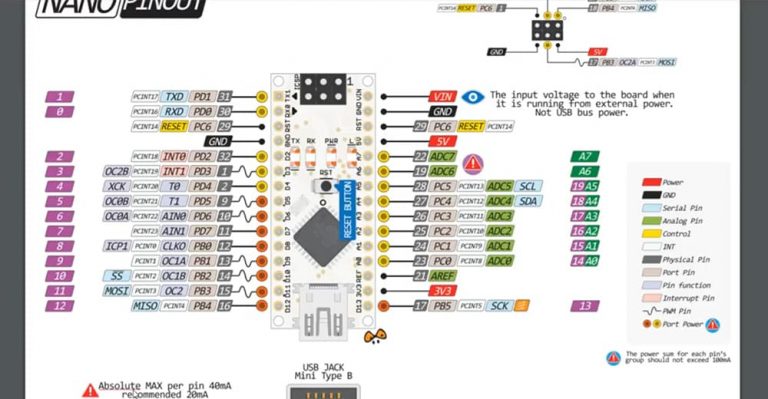
Let’s change a little bit the approach and read an input signal. Blinking LEDs, making sound with the Buzzer, they are all considered output. Up to this point, our experience as been too one-sided.
ARDUINO NANO PINOUT NUMBERS HOW TO
On the same line of experiments, let’s now learn about logic states, as well as how to work with data input devices.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
